PARP inhibitors in Prostate Cancer and the latest developments
Hi, my name is Dr Neeraj Agarwal. I'm a Professor of Medicine and Director of Genito-Urinary Oncology Program at the Huntsman Cancer Institute, University of Utah in Salt Lake City, United States of America.
Today, I'm going to talk about development of PARP inhibitors, or poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors, in the context of advanced prostate cancer.
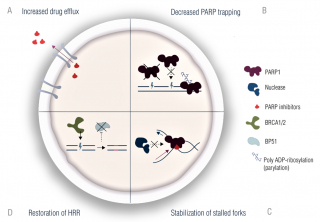
We know that cells which harbour deficiencies or defects in DNA repair genes, more specifically homologous recombination repair genes, excessively rely on poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase to survive.
In this context, regardless of the tumour types, if we target these cells with inhibitors of PARP enzyme it can lead to lethality in the cells and tumour cell death.
Based on this principle multiple PARP inhibitors have been developed in prostate cancer which have led to approval of two PARP inhibitors, olaparib and rucaparib, in the context of metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer which has already progressed on novel hormonal therapies such as enzalutamide or abiraterone or novel hormonal therapy and chemotherapy.
So olaparib is approved after disease progression on novel hormonal therapy and rucaparib is approved after disease progression on novel hormonal therapy, as well as chemotherapy with docetaxel.
However, we also know, based on the preclinical data, there is a rationale for developing PARP inhibitors in patients who do not have DNA repair gene mutations in their cancers.
Androgen receptor and PARP seem to have interdependency. Androgen receptor targeting can create a BRCAness phenotype, and PARP inhibitors can make prostate cancer cells excessively reliant or excessively sensitive to targeting by androgen receptor inhibitors based on the preclinical rationale.
Based on this data, two phase 3 trials were reported in the 2022 Genito-Urinary Oncology Symposium, also known as GU ASCO.
MAGNITUDE trial, reporting improved radiographic progression-free survival with the combination of abiraterone and niraparib versus abiraterone with placebo in patients who were biomarker positive who were harbouring DNA repair gene mutations in their cancers. This benefit was most pronounced in those patients with prostate cancer who had BRCA1 and BRCA2 mutations. And we did not see any benefit with this combination in patients who did not have homologous recombination repair gene mutations.
Intriguingly, in the same meeting, PROpel trial was presented, which was also a phase 3 trial with a combination of abiraterone with olaparib showing benefit. Significant improvement in radiographic progression-free survival compared to abiraterone with placebo in patients with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer regardless of presence of underlying DNA repair gene mutations.
Both MAGNITUDE trial and the PROpel trial were conducted in the first-line, castration-resistant prostate cancer setting.
We also know that there are two trials going on in metastatic castration-sensitive prostate cancer in patients who are harbouring DNA repair gene mutations in their tumours.
In the AMPLITUDE trial, the combination of abiraterone and niraparib is being tested against abiraterone plus placebo.
In the TALAPRO-3 trial, the combination of enzalutamide with talazoparib is being tested compared to enzalutamide plus placebo. The endpoint in both trials is radiographic progression-free survival.
Time will tell if these trials are positive and if they are PARP inhibitors will continue to move up in the setting of advanced prostate cancer.
Please also refer to the enclosed slides which have been uploaded with this talk highlighting the role of PARP inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer. Thank you very much for your kind attention.




 Downloadable
Downloadable 









 5 MIN
5 MIN
 Jun 2025
Jun 2025